Open Article in New Tab
Ethernet technology has come a long way since its inception in the late 1970s when early Ethernet operated at 10 Mbps, which was considered fast for its time. As digital demands increased, so did the need for faster data transfer speeds, leading to the introduction of Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps) and eventually Gigabit Ethernet ( 1 Gbps ), which has been the standard for home and office networking for over 20 years. Over these years, Ethernet continued to evolve, with standards being developed to handle even higher speeds but most often being isolated to the server room, and cloud computing. Today, technologies like 2.5 Gbps and 5 Gbps Ethernet have developed from 10 Gbps Ethernet, catering to modern high-bandwidth applications in both home and office environments. These advancements make it easier than ever for users to connect and transfer data at speeds that support the demands of video streaming, gaming, and extensive network tasks with higher reliability and lower latency than WiFi.
Upgrading a whole network from Gigabit to 2.5Gbps or faster can be costly and time consuming, but it doesn’t have to be done all at once. We have released both 2.5Gbps and soon 5Gbps USB Ethernet adapters that can be used with both notebook computers and desktops to provide up to five times faster Ethernet speeds than the built-in network controller, without having to install any new PCIe cards. Both of our high-speed Ethernet offerings are backwards compatible with current Gigabit Ethernet and in many cases can use the same network cables, however we do recommend replacing Category 5 and Category 5e cables with at least Category 6a or Category 7 cables to ensure future compatibility with both 5Gbps and 10Gbps Ethernet. Desktop 2.5Gbps and 5Gbps Ethernet switches are also coming down in price and can be used to quickly upgrade the network throughput between nearby computers.
As you make the upgrade process there are some steps that can be taken to ensure the network throughput is maximized between the 2.5Gbps or faster computers.
Maximizing the performance of a 2.5Gbps Ethernet network can enhance both speed and reliability, especially for power users who value efficiency and seamless connectivity in a busy IT environment or at home for the fastest home media center. Here are some best practices for small 2.5Gbps and 5Gbps network setups:
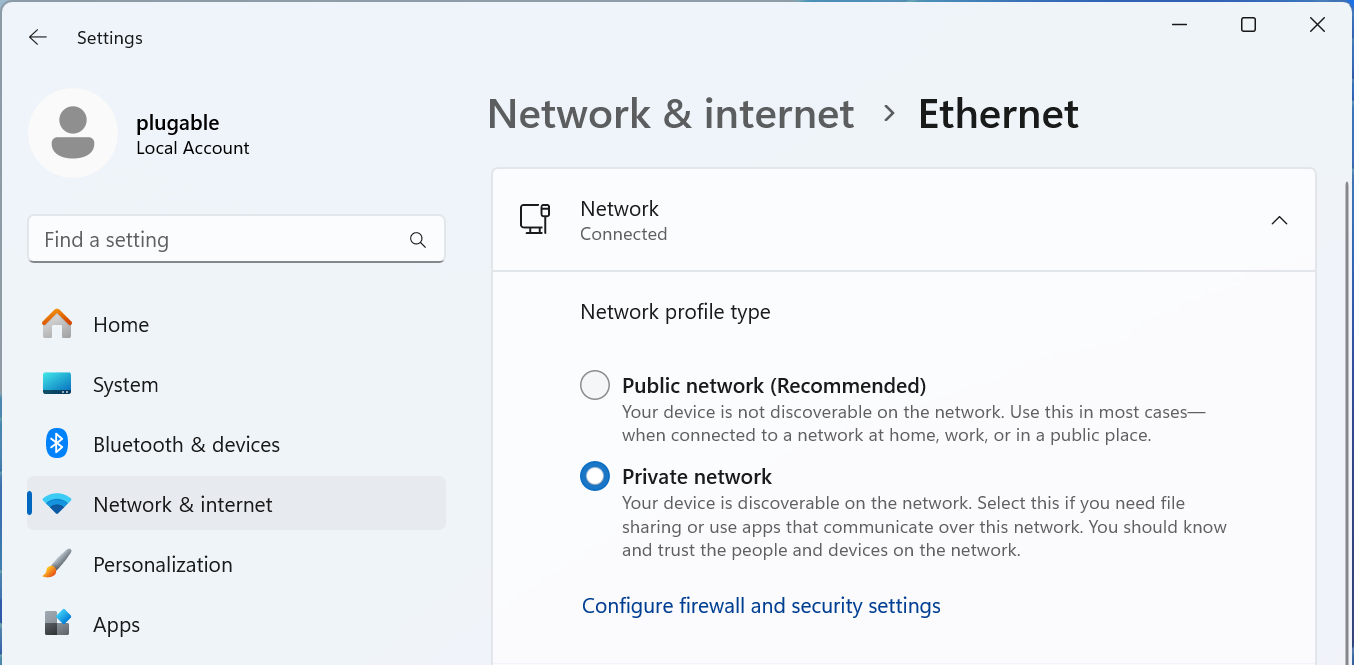
Upgrade Network Infrastructure for Compatibility
Switches and Routers: Ensure your network infrastructure, particularly switches and routers, supports 2.5Gbps or 5Gbps Ethernet. Many older devices are limited to 1Gbps, which will bottleneck the system.
This is most important between the computers that need the higher speed, if you have internet speed at or below 1Gbps then upgrading the router will not improve performance, so long as all computers that need faster local area network access are connected to the same 2.5Gbps or faster Ethernet switches.
Cable Quality: Use high-quality Cat 6a cables or better. While 2.5Gbps is designed to work with Cat 5e Ethernet cables, at least for short distances, for longer runs and to ensure the best performance Cat 6, 6a, or Cat 7 are recommended for 5Gbps networks.
Optimize Device Connections and Settings
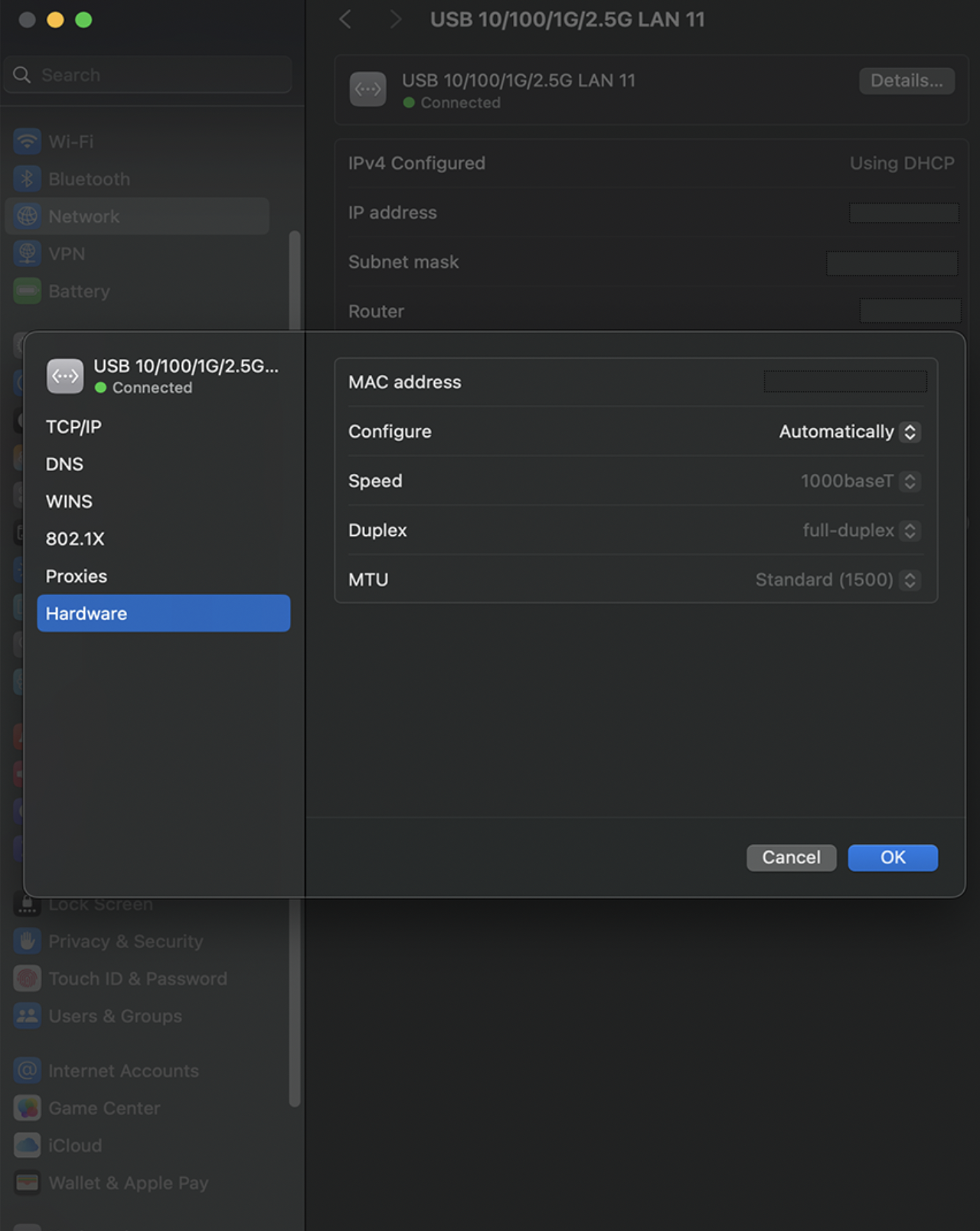
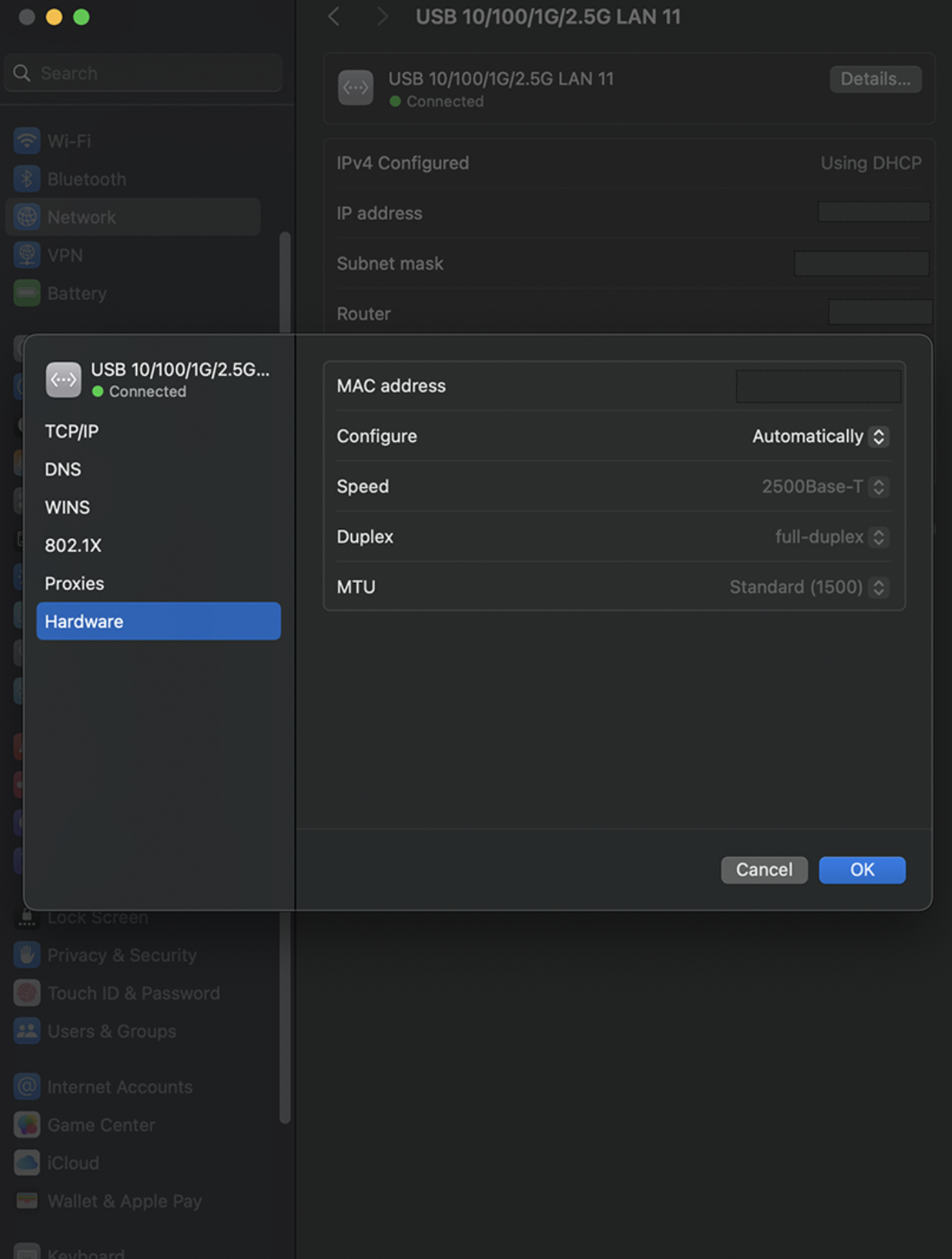
NIC Configuration: Adjust your network interface card (NIC) settings to ensure optimal performance. This may involve tweaking parameters such as jumbo frames or flow control for maximum efficiency.
Ethernet data frames with more than 1500 bytes of data are called “jumbo frames”. Setting a larger frame size packs more data into each frame and can potentially reduce the CPU overhead, however to function it must be enabled on both endpoints and supported by all networking hardware in between. For most users there will be no noticeable difference in network performance, however in some specific cases like when a home server is transcoding and streaming video it can help to reduce the CPU overhead of the entire process. This can best be enabled on short point-to-point networks rather than sprawling networks, as packet loss with jumbo frames enabled causes significantly worse slowdowns than with standard frame sizes.
Flow control allows for the receiving system to transmit a pause request to the transmitting system to prevent data loss. This is necessary when multiple computers are communicating to the same server as there is generally not enough bandwidth to service all requests simultaneously, however it can be disabled in a point-to-point network setup where both computers are directly connected and both computers can handle full-speed data throughput. QoS - Quality of Service offers an alternative to Flow Control but requires significantly more setup often including managed switches and may not be an effective choice for the home and small office networks.
Driver and Firmware Updates: Keep all drivers and firmware updated for your network adapters, switches, and routers. This reduces potential compatibility issues and improves performance. Firmware updates are also important for maintaining network security, vulnerabilities in router firmware have been historically exploited to create network back doors, to exfiltrate data, as well as creating bot-nets for DDoS - Dedicated Denial of Service attacks on websites.
Drivers for Plugable devices can be found on our product pages, under the "Downloads" tab.
Consider Network Segmentation
For a network with mixed-speed devices (1Gb, 2.5Gbps, 5Gbps and 10Gbps), segmenting traffic can prevent slower devices from dragging down performance. This can be done physically by using gigabit Ethernet switches separate from 2.5Gbps or 5Gbps switches then bridging the switches together, or virtually by setting up virtual LANs (VLANs) with a managed Ethernet switch. VLANs can help allocate 2.5Gbps and 5Gbps connections exclusively for high-bandwidth tasks while lower speed devices can utilize secondary gigabit Ethernet ports on the server or client computers.
Leverage Multi-Gig Capable Devices for Key Applications
Identify the devices that will benefit the most from 2.5Gbps and faster connections, such as NAS - Network Attached Storage systems with integrated 2.5Gbps or 5Gbps Ethernet, high-performance workstations or desktop replacement notebooks with USB Ethernet adapters, or servers with multi-port bonded Ethernet controllers handling large data transfers. Connect these devices directly to a switch that can take advantage of the higher network throughput to ensure they receive the best performance possible.
Future-Proofing with 2.5Gbps-capable or faster Docking Stations and USB Ethernet Adapters
Many Plugable docking stations now support 2.5Gbps Ethernet, which could be ideal for enhancing productivity for hybrid work setups, at home, or in the classroom by enabling high-speed, wired connectivity. Plugable’s docks also simplify integration across Windows and Chrome OS devices, which can be especially helpful in mixed-device environments.
USB Ethernet Adapters
- 2.5Gbps USB 3 Ethernet Adapter ( https://plugable.com/products/usbc-e2500 )
- 5Gbps USB 10Gbps Ethernet Adapter ( https://plugable.com/products/usbc-e5000 )
- 1Gbps USB 3.0 Standard-A and Type-C Ethernet Adapter ( https://plugable.com/products/usb3-e1000 https://plugable.com/products/ubsc-e1000 )
Thunderbolt and USB4 docking stations
- USB4 Dual 4K Docking Station ( https://plugable.com/products/ud-4vpd )
- Thunderbolt 4 Quad Display Docking Station ( https://plugable.com/products/tbt4-udz )
- Thunderbolt 4 and USB4 HDMI Docking Station ( https://plugable.com/products/tbt4-udx1 )