







Hassle free, 2-Year Warranty
Fast, Free Shipping on Orders $35+
Lifetime Technical Support
30-Day Money Back Guarantee
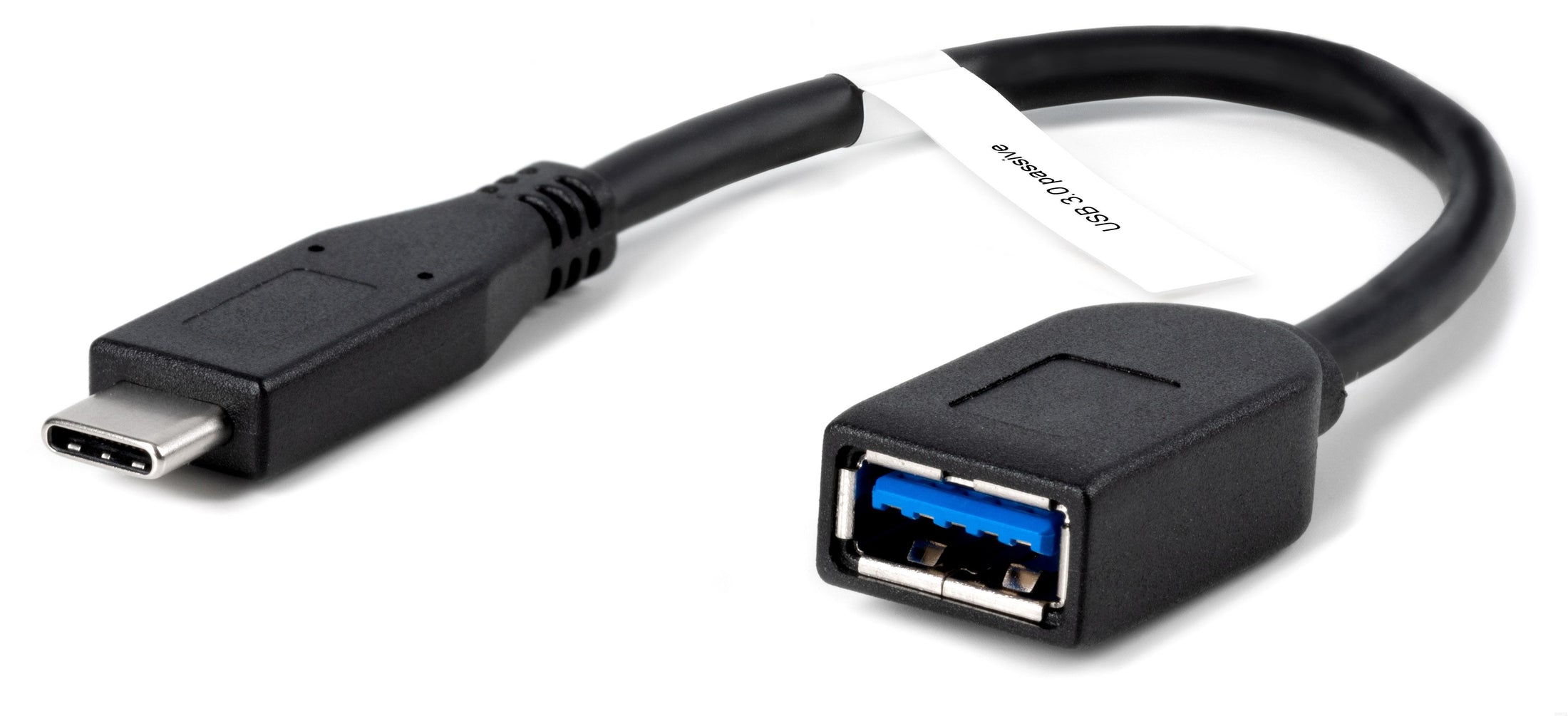
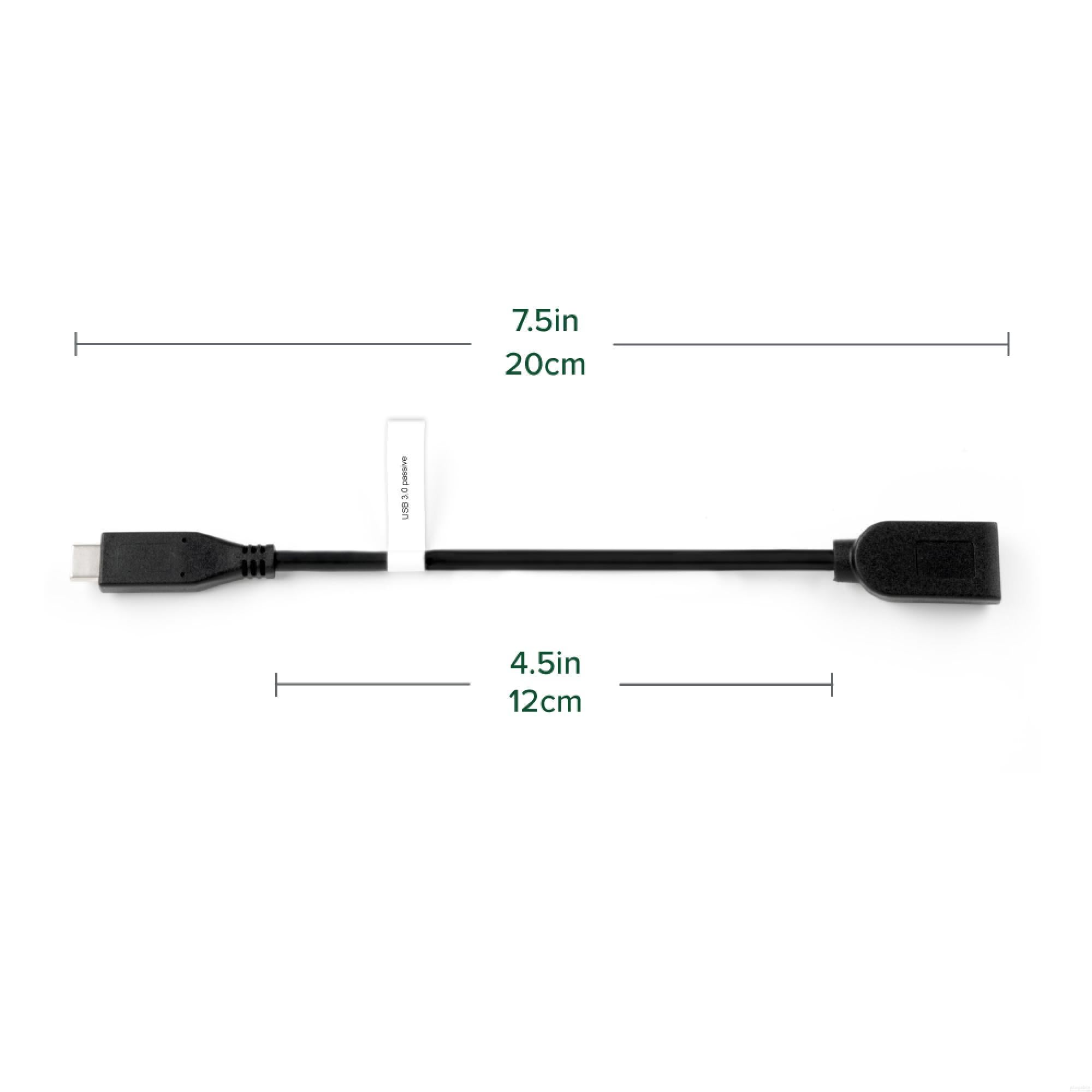
Plugable USB 3.0 Passive Type-A to Type-C Cable (6in/15cm)
$9.95 USD
SKU: USBC-AF3Amazon Rating : (430 Reviews)
Features
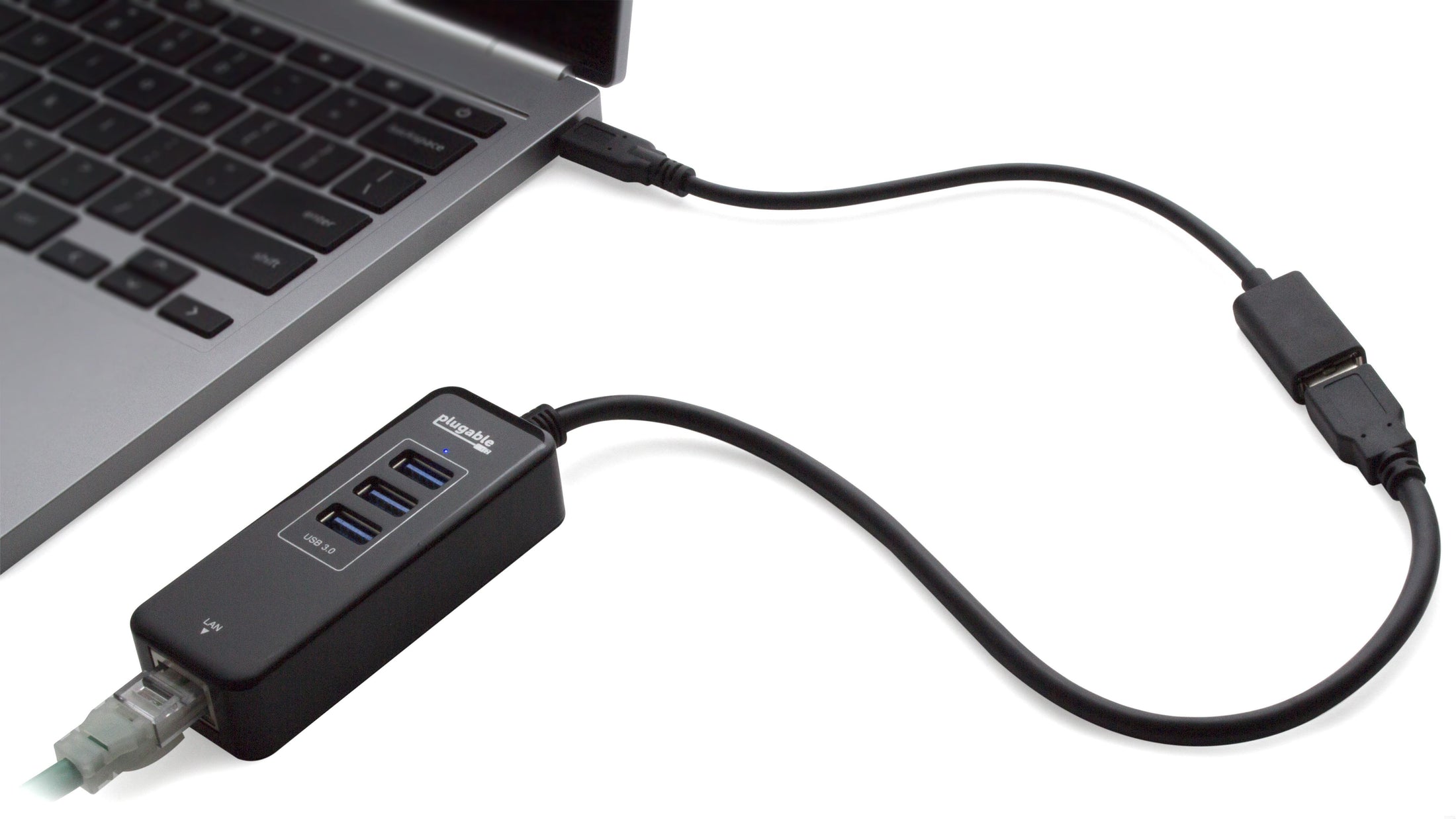
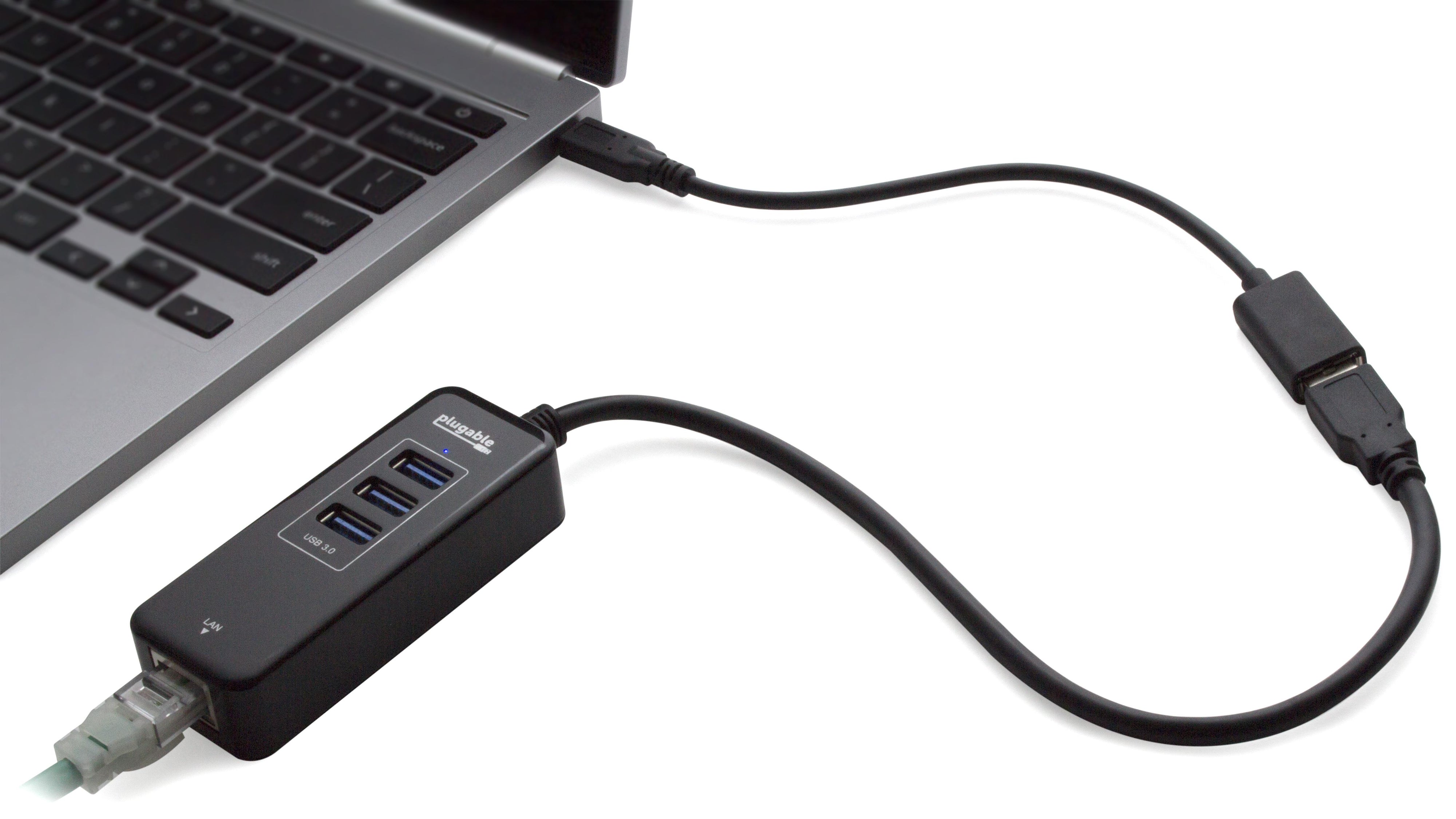
- Universal Compatibility— Connect any USB C, USB4, Thunderbolt 3, or Thunderbolt 4 enabled laptop, phone, or tablet to a legacy USB 3.0 device or peripheral (flash drives, keyboards, mice)
- User Friendly— Plug-and-play USB to USB C adapter for home or office use, 20cm cable designed to fit side-by-side on laptops with two neighboring USB C ports. This also works well as a USB connection to phone adapter.
- Performance— This Plugable USB to USBC adapter cable allows for transfer speeds up to 5Gbps, backwards compatibility, syncing, and charging.
- Compatible With— MacBooks, most Windows systems with Windows 10 or newer, and most Chromebooks running ChromeOS 100 or newer that has a USB C port. Macbook Pro 13" / 14" / 15", 16", MacBook Air, MacBook Retina, MacBook M1 / M2 / M3, HP Spectre x360 / Pavilion / Envy, Dell XPS / Precision / Latitude, Lenovo ThinkPad / IdeaPad / Yoga / Flex, Surface Pro 7 / 7+ / 8 / 9, Surface Laptop 3 / 4 / 5 / Studio / SE, Surface Go / Go 2 / Go 3, LG Gram, Acer Aspire / Swift / Spin, ASUS Zenbook / Vivobook
- 2-Year Coverage, Lifetime Support— Every Plugable product, including this USB C to USB adapter cable, is covered against defects for 2 years and comes with lifetime support. If you ever have questions, contact our North American-based team - even before purchase
Free 3-Day Continental U.S. Shipping on Orders Over $35!





